Medication Management: Tips for Safe and Effective Use

Medications play a crucial role in managing health and treating illnesses, but improper use can have serious consequences. Studies show that four out of ten older adults who take multiple medications do not adhere to their prescriptions as directed. However, medication adherence can be an issue for people of any age. To ensure your medications work effectively and safely, follow these key guidelines.
Ask Questions
Understanding your medications and how to take them is crucial. When prescribed a new medicine, make sure to ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist:
- What is the name and active ingredient of the medicine?
- What is its purpose and the correct dosage?
- What does it look like and when does it expire?
- Are there any side effects or warnings?
- Can it be taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding (if applicable)?
- Are there any interactions with other medicines or foods?
Keep a Medicine List
Maintain a comprehensive list of all your medications, including prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements. Keep this list with you and update it regularly. Share it with your doctor, nurse, and pharmacist to ensure everyone is aware of what you’re taking. This will help avoid potential interactions and errors.
Follow Directions
Strictly adhere to the instructions provided with your medication. Taking too much or too little can be harmful.
- Read the label carefully and follow the prescribed dosage.
- Never skip doses or stop taking medication without consulting your healthcare provider.
- Avoid taking medicine in the dark or without proper identification to prevent mistakes.
- Check expiration dates regularly and avoid using expired medications.
- Use a pill organizer to keep track of your daily doses and avoid missed or duplicated doses.
Filling Your Prescription
Below is an example of information that you will typically see on a prescription label. Your prescription label may have a different format than the one shown, but the prescription number is usually printed in the upper left corner of the label.
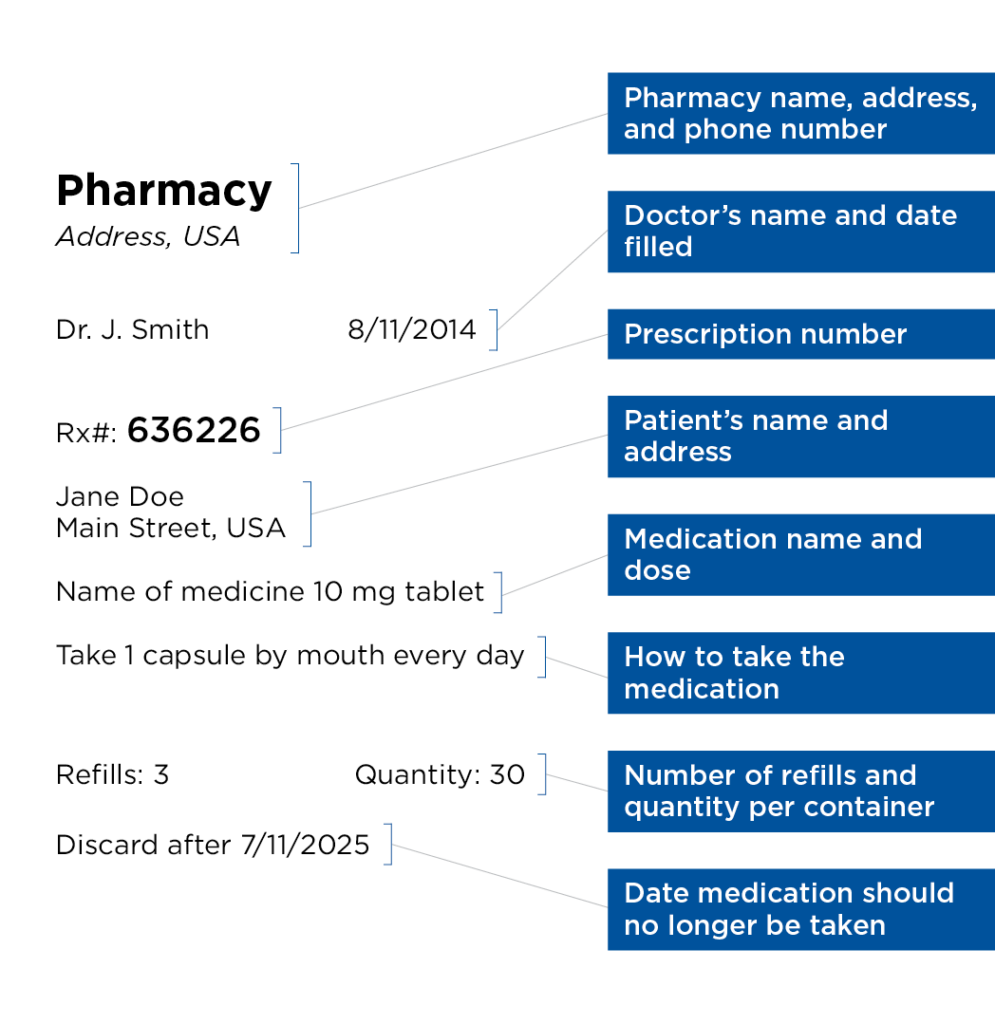 Doctors and pharmacists often use abbreviations or terms that may not be familiar to you. Here is an explanation of some of the most common abbreviations you will see on labels of your prescription medications:
Doctors and pharmacists often use abbreviations or terms that may not be familiar to you. Here is an explanation of some of the most common abbreviations you will see on labels of your prescription medications:
- Rx means “prescription”
- prn means “as needed”
- qd means “every day,” bid means “twice a day,” tid means “three times a day,” qid means “four times a day”
- ac means “before meals,” pc means “after meals”
- hs means “at bedtime”
- po means “by mouth”
- ea means “each”
Ask your pharmacist to explain any terms or abbreviations on your prescription medication label that you don’t understand.
Sources: fda.gov, nia.nih.gov
